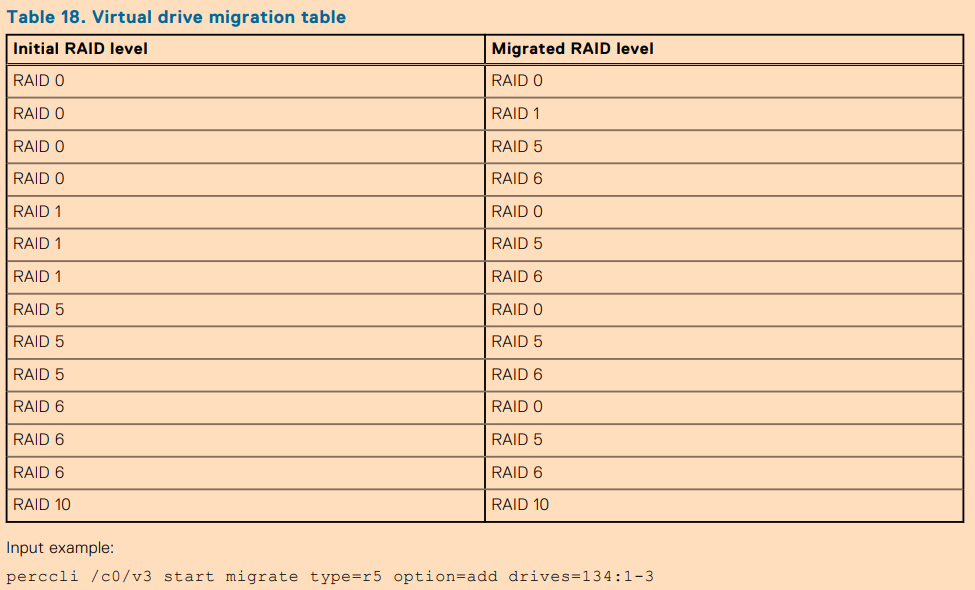
You want to install Windows 11 without a Microsoft Account. After the initial install, upon reboot, you will be presented with this screen:
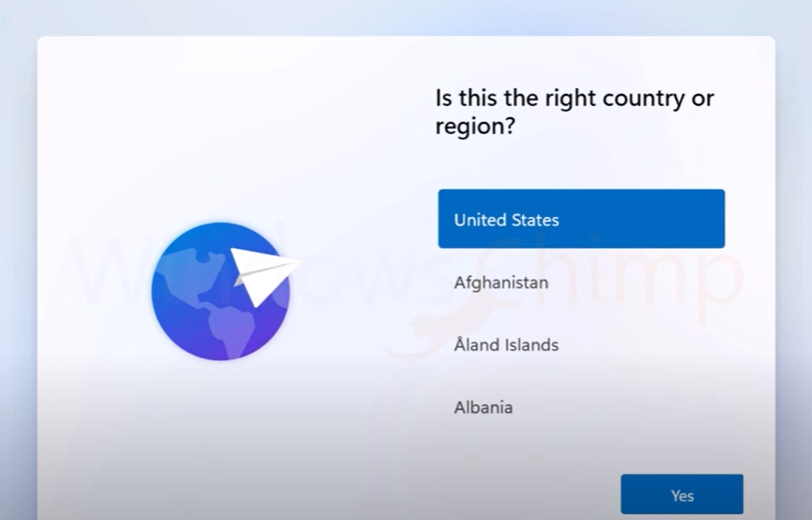
Type: SHIFT F10. This will open the command prompt. At the command prompt type:
start ms-cxh:localonly
You will then be presented with the screen to create a local account.
Enjoy 🙂